Network Attacks
In the Network Protection > Network Attacks section, Network Attack Defense provides a security layer based on a Bitdefender technology that detects and takes actions against network attacks designed to gain access on endpoints through specific techniques such as: brute-force attacks, network exploits and password stealers.
Note
The Network Attack Defense module is available for:
Windows for workstations
Windows for servers
On Windows servers, Network Attack Defense detects and prevents RDP brute-force attacks by scanning incoming connections on the RDP ports to identify authentication anomalies. Network Attack Defense also scans web traffic when used with Content Control.
macOS
Linux
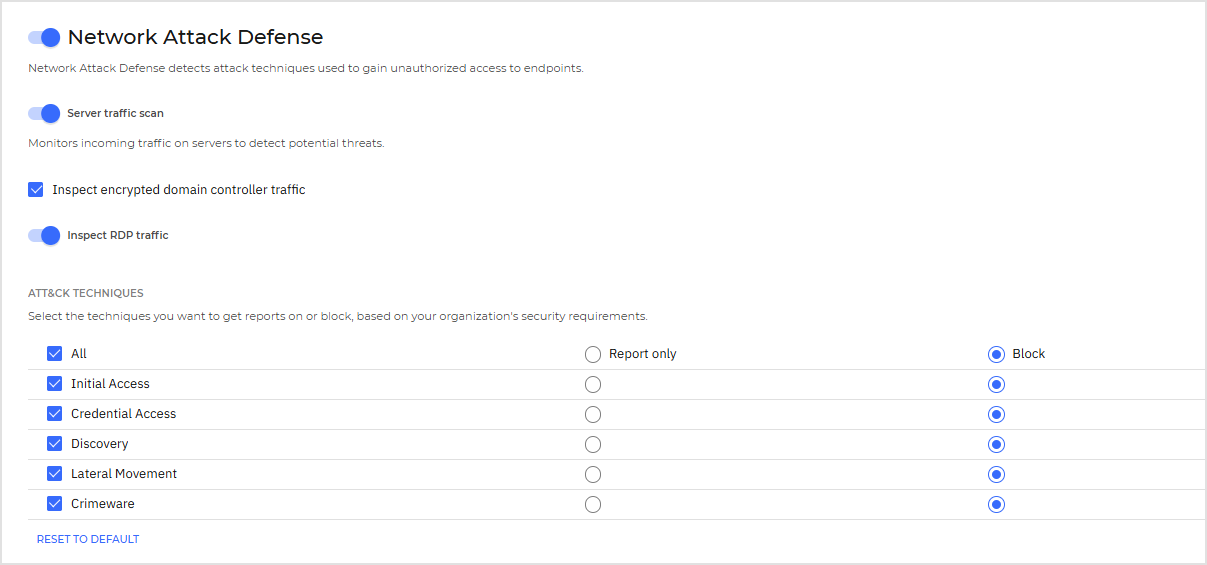
To configure Network Attack Defense:
Click the toggle to enable Network Attack Defense.
Select Server Traffic Scan to monitor incoming traffic on servers for potential threats across the SMB, RPC, Kerberos, LDAP, and WinRM protocols.
Select Inspect Encrypted Domain Controller Traffic to scan encrypted traffic over the SMB, RPC, and Kerberos protocols.
Select Inspect RDP Traffic to extend SSL scanning to RDP protocol.
Note
To enable this option, first activate encrypted traffic interception in the General section.
Select the corresponding checkboxes to enable protection against each network attack category. The network attack techniques are grouped according to MITRE's ATT&CK knowledge based as follows:
Initial Access - the attacker gains entry within a network by various means, including vulnerabilities of public-facing web servers. For example: information disclosure exploits, SQL injection exploits, drive-by download injection vectors.
Credential Access - the attacker steals credentials like usernames and passwords to gain access into the systems. For example: brute-force attacks, unauthorized authentication exploits, password stealers.
Discovery - the attacker, once infiltrated, tries to obtain information about the systems and the internal network, before deciding what to do next. For example: directory traversal exploits, HTTP directory traversal exploits.
Lateral Movement - the attacker explores the network, often by moving through multiple systems, to find the main target. The attacker may use specific tools to accomplish the objective. For example: command injection exploits, Shellshock exploits, double extension exploits.
Crimeware - this category comprises techniques designed to automate cybercrime. For example, Crimeware techniques are: nuclear exploits, various malware software such as Trojans and bots.
Select the actions you want to take against each category of network attack techniques from the following options:
Block - Network Attack Defense stops the attack attempt once detected.
Report only - Network Attack Defense informs you about the detected attack attempt, but it will not try to stop it.
Note
The Server Traffic Scan and Inspect Encrypted Domain Controller Traffic functionalities will be available with the GravityZone version 6.63.
You can easily restore the initial settings by clicking the Reset to default button at the lower side of the page.
Details about network attack attempts are available in the Network Incidents report and in the Network Incidents event notification.