“Didn’t you say you had it under control?” Discover why smart security teams choose GravityZone — before the chaos hits. Learn More >>
Remote Browser Isolation is a security technology that loads all web traffic away from a user and then sends them a secure version of the page. It’s a zero-trust approach to web security that’s especially effective against zero-days APTs, and other emerging threats.
Born in the early 2010s, browser isolation was created because traditional gateway-level security solutions couldn’t keep up with sophisticated online threats. By isolating all web browsing away from a user’s device, any malicious page or document presents a much lower risk.
Most commonly, RBI will use a client-server infrastructure to load pages remotely and then stream the content to the user.
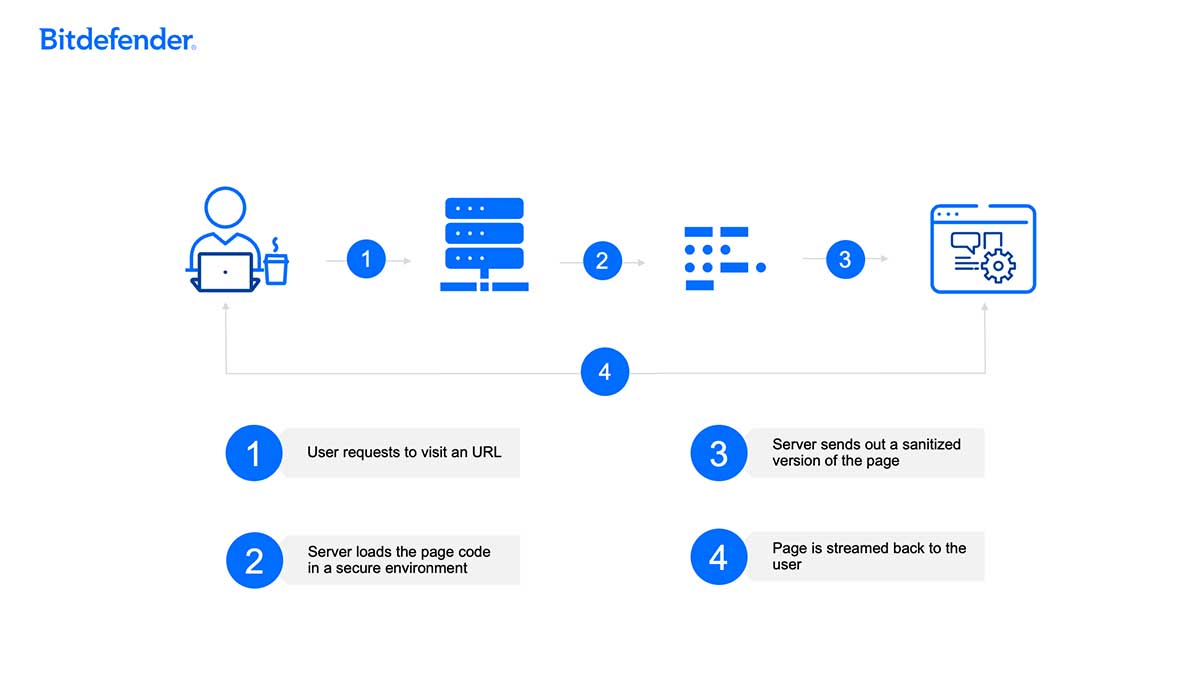
How Remote Browser isolation (RBI) works
Other browser isolation solutions might be deployed on premises, not in the cloud. They might recreate pages locally, rather than streaming the content. But the common throughline is, as the name suggests, isolating potentially malicious web content from a user’s device.
Remote Browser Isolation can be very effective against web threats. It can mitigate the impact of technical exploits, like:
Browser isolation can also minimize the impact of social engineering, in cases of:
Most business tools today, from document editors to analytics dashboards, are accessed from a browser. That’s why companies need to invest in a browser isolation tool. It’s a proxy between your enterprise’s devices, and the world wide web.
Browser isolation has evolved in recent years due to increasing reliability on cloud services. As a result, there are a lot of ways to classify browser isolation technologies, based on where pages are loaded and the infrastructure of the BI solution.
Remote Browser technology can be broken down in three categories, based on how web content reaches the user.
For the right enterprise, Remote Browser Isolation is the best solution against web threats. However, web isolation has its drawbacks, such as increased latency if not properly configured.
To help you make the best decision for your enterprise, here’s an overview of RBI’s benefits and drawbacks.
Better user experience and less admin overhead. Without an RBI solution, companies might impose strict limits on the browsing activities of employees. With RBI, this aggressive stance on unknown, potentially malicious pages is not necessary.
RBI can present drawbacks for companies, including:
Remote Browser Isolation is a strong, zero-trust approach to neutralizing web threats. It can defend against cross-site scripting, clickjacking, phishing, and many more.
It’s not perfect. It won’t prevent all types of social engineering, and you can see some friction implementing it. But if you partner with a reputable RBI provider, you’ll mitigate any worries about latency, compatibility, or difficult integration.
If you want to find out more about cybersecurity, read our InfoZone guide on Endpoint Security.
Bitdefender licenses its Remote Browser Isolation to partners that want zero-trust web security. It’s part of our larger Sandbox Service, and it’s very easy to implement. Partners only need to account for a few API calls to set-up powerful RBI environments.
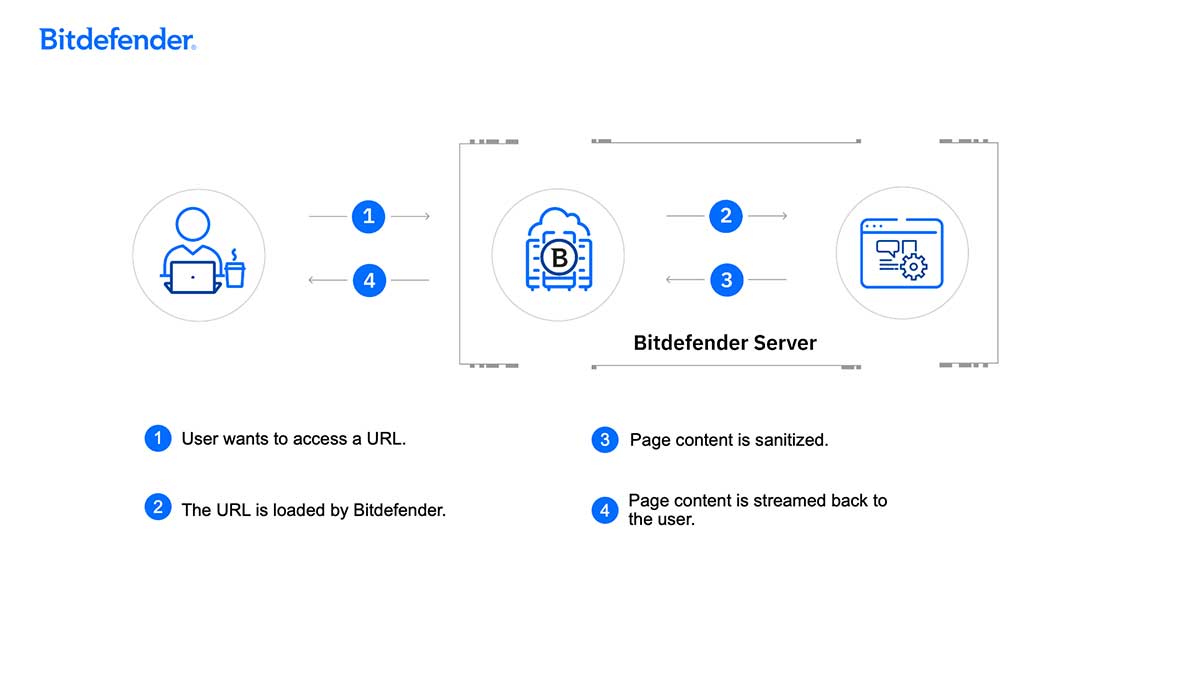
How Bitdefender RBI works
Bitdefender RBI comes with extended session durations, timeout notifications, copy-and paste, as well as download capabilities.
At the moment, Bitdefender RBI is only available to a limited number of partners.
Inquire about our technology licensing portfolio to see if you qualify.
Remote Browser Isolation is a web security technology that can protect users from browser-based threats. It offers a zero-trust approach to web security, making it attractive for companies that want to improve their posturing against common web threats.
Remote Browser Isolation protects the endpoints of users against online threats. Secure Web Gateway (SWG) analyzes traffic coming into a network at the application layer. RBI and SWG are somewhat redundant – but they complement each other, because RBI employs a zero-trust approach, making it more effective against zero-days.
The main advantage of Remote Browser Isolation is protection against emerging or advanced web threats. Because it isolates all user traffic, it can neutralize clickjacking, cross-site scripting, and even some forms of social engineering.