The Ransomware Economy Is Thriving in the Mid-Market

Ransomware has grown from a small industry driven by hobbyist hackers into a thriving underground economy. It has become more accessible than ever, powered by high-speed internet around the globe and specialized threat actors who rent out ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) to profit from extortion.
Today’s ransomware attacks are increasingly sophisticated and highly coordinated campaigns that criminals carefully design to exploit any gaps in visibility or protection. According to Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), ransomware incidents surged by 37% year-over-year. The DBIR says the greatest impact is on SMBs.
“Ransomware is also disproportionally affecting small organizations. In larger organizations, ransomware is a component of 39% of breaches, while SMBs experienced ransomware-related breaches to the tune of 88% overall."
Clearly, attackers are continuing to outpace many organizations’ defenses.
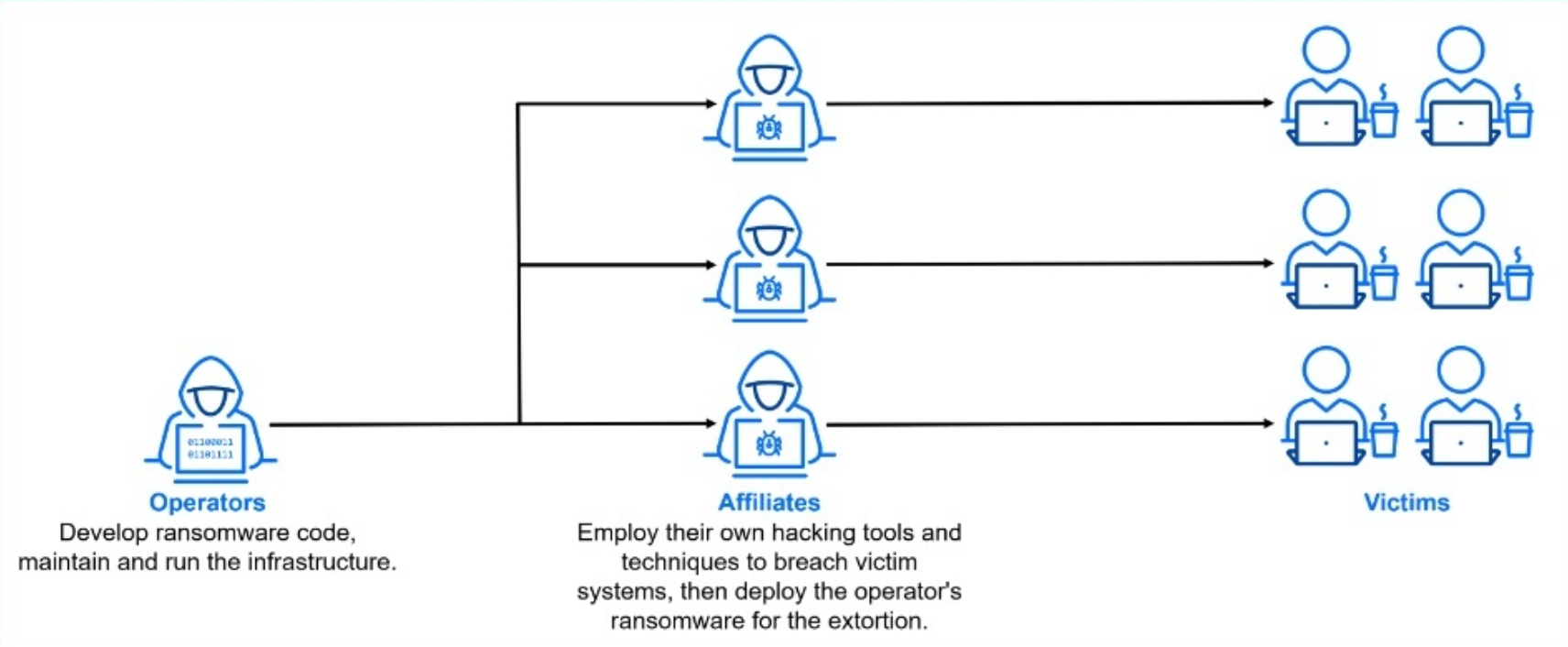
The Ransomware Ecosystem
The modern ransomware economy consists of specialized groups, including operators, affiliates, developers, brokers, and service providers. Many operate like legitimate businesses, making them harder to defend against.
Operators
Operators are the center of the ransomware economy. They coordinate the moving parts of attacks to maximize impact and profit, and often run their services like sophisticated businesses. They are responsible for developing and maintaining new tools and ransomware strains, and packaging them into kits that they market and sell to affiliates.
Beyond creating tools, operators also run campaigns, manage negotiations, and decide whether to sell, leak, or hold data for ransom.
Affiliates
Affiliates are responsible for distributing the ransomware. In some cases, their role is to gain access to target networks and establish footholds, then move laterally through the network to identify valuable data to carry out extortion. In other cases, they leverage previously established footholds into an organization to carry out their attacks.
If the attack succeeds and the victim pays the ransom, the operator and affiliate typically split the profits. That arrangement incentivizes affiliates to deploy attacks as efficiently and effectively as possible.
Other Specialized Ransomware Roles
Other specialized roles operating behind the scenes and helping the ransomware economy to thrive include:
Developers
Developers monitor security tools closely to identify weaknesses that future versions can exploit.
Initial Access Brokers (IABs)
IABs facilitate easier access to corporate networks by selling stolen credentials and backdoors. They also provide reconnaissance details, such as network structure and user privileges, to buyers.
Service Providers
Service providers offer a range of services, such as VPNs and hosting, that help cybercriminals hide their transactions and communication. They also supply phishing and exploit kits and assist with converting ransom payments into fiat currency anonymously. Developers create and update ransomware code, producing new variants designed to evade detection.
The Anatomy of Ransomware
Most ransomware attacks follow a predictable pattern. Understanding these patterns can help you anticipate the movements of threat actors and defend your organization more effectively.
Initial Access
An attacker starts by gaining entry into your environment. Some of the most common entry points include:
- Phishing and credential compromise: Attackers impersonate legitimate institutions in an attempt to trick victims into revealing their credentials. They often use calls, emails, or text messages to carry out these schemes.
- Weak or stolen credentials: Threat actors typically obtain these through breaches or brute force attacks.
- Exploits: This is when attackers take advantage of unpatched software vulnerabilities in your system.
In some cases, attackers may employ multiple techniques in a single attack to increase their chances of success.
Ransomware Attack Progression
Once attackers have gained access to your organization’s system, they work to expand their foothold. They typically move laterally across your system, searching for high-value targets to exploit.
Attackers often attempt to escalate privileges to gain administrative access, so they can disable your security mechanisms and gain greater control over your systems. They will also evaluate your organization’s security posture to identify weaknesses and figure out ways to maintain access, even if part of their attack is discovered or blocked.
Extortion and Impact
Once attackers gain control, they move to extortion by encrypting your sensitive data and blocking access until you pay the ransom. Many modern attackers use double extortion, exfiltrating the data and then threatening to publish or sell your data if you refuse to pay.
Such attacks severely disrupt business operations and can lead to catastrophic financial and reputational consequences that are difficult to recover from. They can also expose your organization to regulatory penalties and legal liabilities.
Key Defender Challenges
The ransomware economy is constantly changing, driven by the rise of remote work and the increasing use of AI in cybercrime. These changes present unique ransomware challenges for mid-market organizations with limited IT resources.
Expanding Attack Surface
The rise of hybrid working has increased the number of potential entry points for attackers. Organizations now need to secure identities, IoT devices, mobile devices, cloud applications, and traditional endpoints and servers. Misconfiguring or forgetting to properly manage even one of these entry points presents an opportunity for attackers.
Common Entry Points
Despite the increasing sophistication of many attacks, phishing and credential compromise remain among the most common entry points for attackers.
Phishing relies on humans making mistakes, often by clicking a malicious link or opening a suspicious attachment, allowing attackers to bypass traditional defenses. Meanwhile, credential theft provides attackers with direct access to systems, often through weak passwords, stolen login credentials sold on the dark web, or brute-force attacks.
These entry points can be particularly effective for attackers, as they are often low-cost and allow them to move freely through your system without immediately raising alarms.
Advanced Techniques
In the modern ransomware economy, many attackers employ advanced techniques and sophisticated tools to evade detection. The growth of RaaS has created numerous new ransomware challenges by lowering the barrier to entry and providing even low-skilled attackers with access to professional-grade toolkits for launching complex campaigns.
It also appears that an increasing number of groups are using Living-off-the-Land (LOTL) techniques, which exploit trusted system tools like PowerShell or WMI. Bitdefender analysis of 700,000 incidents of 700,000 incidents revealed that 84% of high-severity attacks involved LOTL binaries. We also conducted an additional analysis of LOTL prevalence across our MDR incidents, which confirmed the trend: 85% of incidents relied on LOTL techniques.
Blending malicious activity with legitimate processes in this manner makes it significantly more challenging for traditional defenses to identify attackers in action.
Emerging Tools
While most ransomware attacks still involve hands-on keyboard operations, the rise of AI is growing the ransomware economy and increasing the number of attacks. Bitdefender Labs recently profiled the Funksec Ransomware group, which was at script kiddie level not long ago. The group posted on dark web forums, asking for ideas and help to join the ransomware economy. A short time later, researchers found that the group had used AI to rapidly upskill its knowledge and methods, and it soon claimed ransomware victims across multiple countries.
Understanding the Modern Ransomware Economy and Its Challenges
The modern ransomware economy is thriving and shows no signs of slowing down. While increasingly sophisticated technology and the rise of AI in cybercrime have made it more challenging for most organizations to defend against attacks, some regulated industries are performing better thanks to their cybersecurity investments.
Learn more about how lean IT teams can overcome ransomware challenges and achieve enterprise-grade protection by reading the Ransomware Protection Solution Guide.
tags
Author
Cristian Iordache is a CISSP and Principal Product Marketing Manager at Bitdefender and has spent more than a decade helping organizations address cybersecurity challenges. He loves to highlight security tips and technologies that are proven to improve security operations efficiency and effectiveness against the most elusive attacks.
View all postsYou might also like
Bookmarks

