How AI and Machine Learning Are Shaping the Future of IoT Security

Exploring how artificial intelligence and machine learning are redefining security for the evolving Internet of Things landscape.
The expanding attack surface of smart devices
Our homes, cars, and workplaces are becoming increasingly smart. While this brings unmatched convenience, it also opens a Pandora’s box, as the concept of smarter devices often equates to “more vulnerable devices.”
The Internet of Things (IoT) – all the doorbells, thermostats, refrigerators, wearables, and even toothbrushes that make up the world of smart devices – expands the attack surface for cybercriminals almost in proportion to the convenience it brings.
With billions of devices projected to be online in the coming years, traditional security solutions alone won’t be enough. Enter artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), two technologies that have opened a new frontier in defending against evolving threats, especially in environments where human monitoring is impractical.
But how do they work in practice? And what does their usage imply for consumers?
Why traditional security falls short in the IoT era
Before we plunge into the promises of AI and ML in securing the IoT landscape, it’s worth understanding why conventional methods struggle with this challenge.
First of all, the sheer volume of devices makes it impossible to manually monitor all network traffic or patch every vulnerability using traditional methods. Then there’s the diversity of devices – the security needs and flaws of a smart toothbrush, for instance, can vary greatly from those of a smart TV. Many devices have proprietary software, different hardware standards and no unified security model.
Last but not least, the limited resources make it impossible to implement traditional security methods. Most IoT devices have minimal processing power and memory, which makes them unsuitable for traditional endpoint protection tools.
These are some of the most important reasons why we need smarter, more adaptive protection. Here’s where AI and ML shine.
AI and ML, a match made in heaven for the IoT world
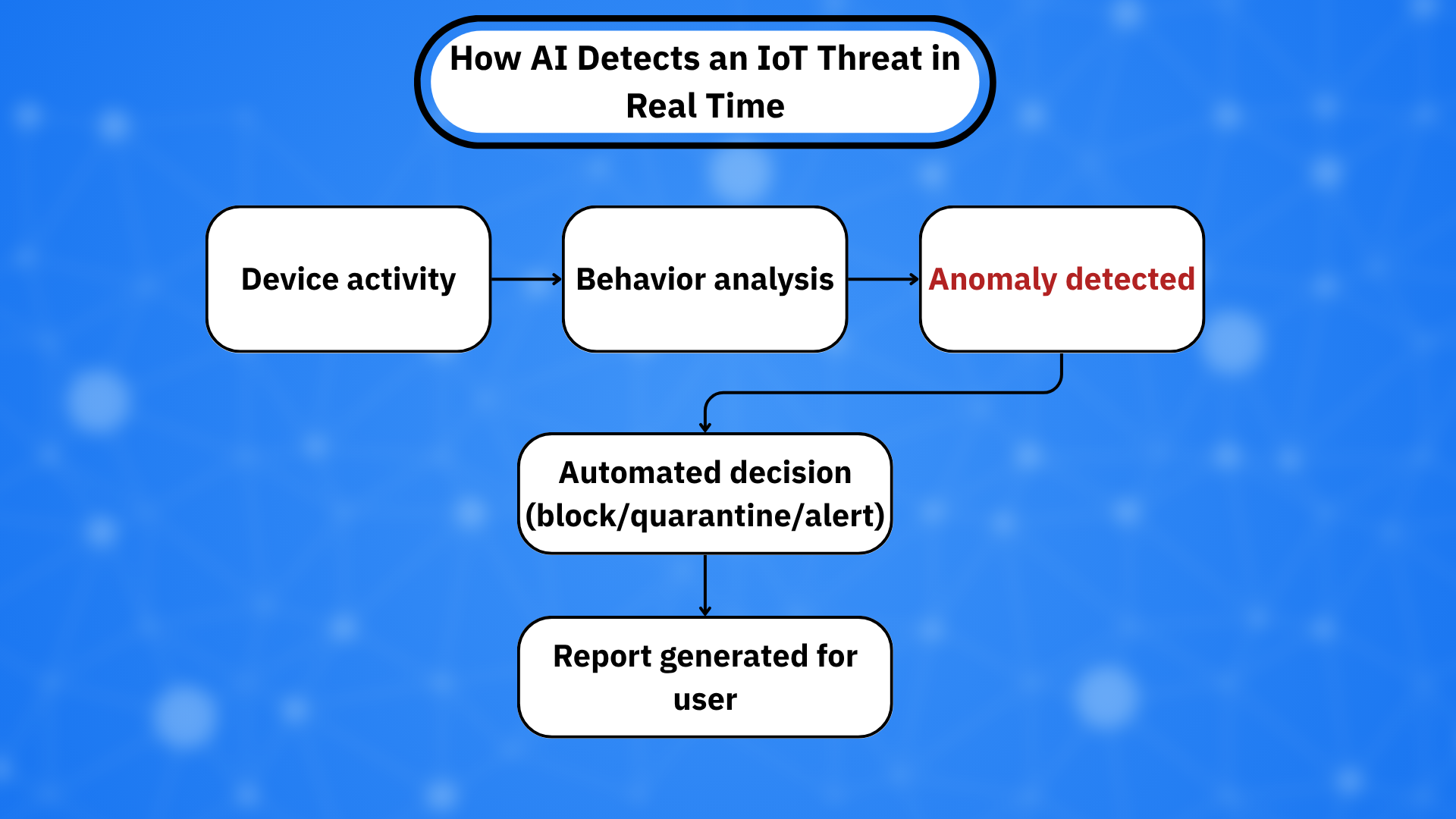
AI and ML systems excel in pattern analysis, anomaly detection, and real-time decision-making. These are all strong points for the chaotic, ever-expanding IoT ecosystem.
Here’s what they bring to the table:
- Anomaly detection: ML algorithms can quickly learn what “normal” behavior looks like for each device, then flag any activity out of those bounds. For instance, a thermostat suddenly trying to contact an unfamiliar server in another country can be immediately flagged as suspicious.
- Real-time threat response: AI-powered systems can block suspicious traffic or quarantine devices instantly, without waiting for human approval.
- Predictive analysis: By analyzing large volumes of data, ML can anticipate threats before they occur. For instance, ML systems can identify the early signs of a botnet forming.
- Automated policy enforcement: AI can help manage device permissions dynamically, adapting access based on context and usage patterns.
Common use cases for consumers
Thanks to user-friendly chatbots and other accessible tools, AI is no longer a distant, enterprise-only concept. In fact, most people probably already use it, one way or another, sometimes without even realizing it.
Here are some real-world applications that leverage AI for IoT security:
- Smart home routers with AI-based intrusion prevention: Certain consumer routers now implement ML features to recognize abnormal traffic from devices and automatically cut them off.
- Voice assistants with intent detection: ML helps identify spoofing attempts or malicious voice commands.
- Security cameras with edge AI features: These devices can detect people, animals and packages, and even recognize if someone is lurking outside your door too long.
- Wearables with behavioral biometrics: Smartwatches or fitness trackers can help verify your identity based on motion, location, or usage patterns.
Although they don’t necessarily make it obvious, these technologies aim to provide peace of mind without requiring users to become security experts.
Challenges and concerns
Despite its obvious advantages, AI isn’t a silver bullet for every underlying security challenge. There are still many issues it can’t tackle, especially from a consumer perspective, including:
- False positives: Anomaly-based systems may sometimes flag normal behavior as suspicious, causing frustration.
- Data privacy: AI needs data to learn. Who controls this data? How is it stored? Is it being sold to third parties? What happens in a data breach?
- Model poisoning and adversarial attacks: Attackers may try to confuse or corrupt the AI itself with rogue prompts and fake training data.
- Opaque decisions: It’s often difficult to understand why AI made a certain choice, as its decision-making process is often invisible to the end user.

What consumers can do today
While we await stronger, more mature AI models for IoT security, you can still take steps to protect your smart home ecosystem or wearable devices on your own.
- Change default passwords: Doing so can significantly increase your chances against an attack leveraging known default passwords.
- Keep firmware updated: Frequent firmware updates (or enabling automatic updates) can protect you from critical security flaws.
- Use network segmentation: Segmenting your network (for advanced users) or placing IoT devices on a guest network (efficient, beginner-friendly method) can help you limit the IoT attack surface.
- Disable unnecessary features: Certain features, such as remote access or voice controls, should be disabled if you don’t use them.
- Monitor your network traffic: Using smart routers or security apps such as NETGEAR Armor can help you keep an eye on your IoT ecosystem.
- Audit your smart home: A monthly IoT security audit can keep your smart home secure.
Even basic cyber hygiene can go a long way, especially when combined with AI-powered tools.
Smarter systems, smarter homes
AI and ML are no longer buzzwords; they’re becoming cornerstones for the next generation of cybersecurity, particularly in complex and decentralized IoT environments. For consumers, this translates into smarter protection that quietly unfolds in the background, adapting and learning without all the micromanagement.
However, consumers must still remain vigilant. While AI can make excellent decisions for you, it’s still important to understand the risks, make privacy-conscious choices, and invest in secure devices and services.
As IoT evolves, expect to see more home ecosystems built around AI threat detection and machine learning-enhanced safety features. Just as antivirus software has become a standard on PCs, AI may soon become the norm for safeguarding smart home ecosystems.
Conclusion
The rise of IoT demands a new kind of protection, one that can keep up with the very threats it faces. AI and ML are both strong contenders for that bill.
Although they’re not silver bullets for today’s security challenges, they do offer a glimpse into a future of more proactive, personalized and silent cybersecurity that works behind closed doors so consumers can focus more on living, instead of safeguarding.
Frequently asked questions about AI and ML in IoT security
What is the role of AI in IoT security?
Artificial intelligence is often used to enhance IoT security by automating processes such as identifying suspicious behavior, predicting threats before they occur or enforcing policies automatically.
What is AI ML security?
AI involves the use of artificial intelligence to protect data and devices in various ecosystems. Machine learning (ML) is a branch of artificial intelligence that involves developing algorithms and models to perform complex tasks without human intervention.
What is the role of AI and ML in IoT?
In IoT, AI algorithms are designed to process data logged by devices in the ecosystem. ML, on the other hand, helps bridge the gap between collected data and AI systems, paving the way for advanced processes like real-time decision making and policy enforcement.
tags
Author
Vlad's love for technology and writing created rich soil for his interest in cybersecurity to sprout into a full-on passion. Before becoming a Security Analyst, he covered tech and security topics.
View all postsRight now Top posts
How Do You Manage Your Passwords? We Ask Netizens
December 18, 2025
Cybercriminals Use Fake Leonardo DiCaprio Film Torrent to Spread Agent Tesla Malware
December 11, 2025
FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA
You might also like
Bookmarks