What is Digital Identity Theft? How to Spot, React and Report it

Identity theft has been around for hundreds of years - probably much longer than historical records show - and the expansion of technology has only made things worse.
The Internet, data breaches and your ever-growing digital footprint enable cyber-criminals and scammers to carry out digital identity fraud at scale.
We are here to help you gear up with essential information to fight against online identity theft. Keep reading for clear, actionable tips from Bitdefender cybersecurity experts.
What Is Digital Identity Theft?
Any digital identity theft definition includes a malicious actor that illegally acquires personal information (date of birth, social security number, credit card details etc.) and uses it for identity fraud (cloning credit cards, applying for loans, extorting the victim etc.).
Online, identity theft works largely as it does offline, with a remarkable difference. The massive volume of information attackers can find about you on the Internet and its level of detail makes their “job” much easier and significantly more lucrative.

What Are the Most Common Types of Digital Identity Theft?
Depending on the type of data involved, there are various kinds of identity theft cyber-criminals engage in:
- Child identity theft where attackers use a minor's identity for illegal personal gains. Children’s social security numbers provide clean records thieves use to secure employment, establish lines of credit, get driver's licenses, or even buy property. This type of fraud has long-term damaging effects and is more prevalent than you realize, with 1 in 10 minors affected in a Carnegie Mellon study of 40,000 children.
- Identity cloning where a thief impersonates you to conceal their own identity for fraudulent purposes. Examples include concealing an individual’s illegal status, hiding from creditors, even discrediting you in front of employers and business partners, along with other unlawful activities.
- Financial identity theft in which the malicious actor uses your financial details to apply for and obtain credit, loans, goods, and services. This is the most common type of identity fraud with both online and offline ramifications.
- Medical identity theft where your medical records are used to steal your health insurance, seek medical attention posing as you, alter your medical history or benefit from medical aid schemes.
- Tax identity theft in which the attacker files a tax return with false information to claim and get the refund into a bank account they control.
- Social media impersonation of both individuals and brands consists of cloning your identity and using it to defraud your connections, extort you to regain access, and many of the threats included in this list.
- Synthetic identity theft in which the malicious actor fabricates an identity to pass various authentication tests government or private organizations enforce. This type is especially insidious because it involves combining real and fake elements (e.g. real social security number plus fake name and birth date) and it can go undetected by both anti-fraud systems and the victim itself.
What Are the Warning Signs of Digital Identity Theft?
Because your digital footprint extends far beyond its visible parts, it is difficult to notice when cyber-criminals profile your online persona and use it for malicious gain.
Here are the signs that indicate that fraudulent activity involves your personally identifiable information:
“Warning signs include getting bills for services that you didn’t commission. You may find online accounts for services you’ve never used - so somebody might be using your identity to create accounts for platforms or services they want to use.
Maybe the IRS notifies you that more than one tax return was filed in your name - which is a felony - and you may end up with legal charges.
You may sometimes even be notified that some information has been compromised in a data breach at a company where you have an account with - and that’s usually one of the signs that your personal data is exposed online.”
Liviu Arsene (Senior E-threat Analyst, Bitdefender)
Other red flags include strange transactions on your bank statement, collection agents contacting you to settle debt you have never taken on and medical bills for services you did not receive.
The sooner you identify an anomaly in your online and offline ecosystem of data, products and services, the faster you can act to reduce its impact.
What Are the Dangers of Online Identity Theft?
Online identity theft examples range from fake social media accounts to child identity theft, with consequences ranging from short-lived effects to long-term impact.
The financial damages include:
- a deteriorated credit score
- having to cancel credit or debit cards, close bank accounts and open new ones
- clearing up issues with debt you did not take on
- handling paperwork and being in contact with institutions such as the IRS or law enforcement
- issues with your revenue if digital identity fraud affects your work.
Emotional impact is also part of the consequences of identity theft. Losing control over your data can be very upsetting.
While there are things you can do to keep safe, some elements will always be outside your control. Take data breaches and their role, for example:
“Most data breaches fuel digital identity theft and it’s not people’s fault. Some scammers are very convincing and could have fooled even the best-trained eye.
We’re interacting with the internet at a pace that we’ve never done before and this increases the chances of us becoming a victim.
Even the most security-aware people might disclose information sometimes. Other times, technology discloses that information for us: missed privacy settings, carriers that get breached and expose phone numbers and other personal information.
Reporting these incidents should be business as usual. It’s like having your car hit in the parking lot. It’s not necessarily your fault and it’s part of being online.”
Bogdan Botezatu (Director of Threat Research and Reporting, Bitdefender)
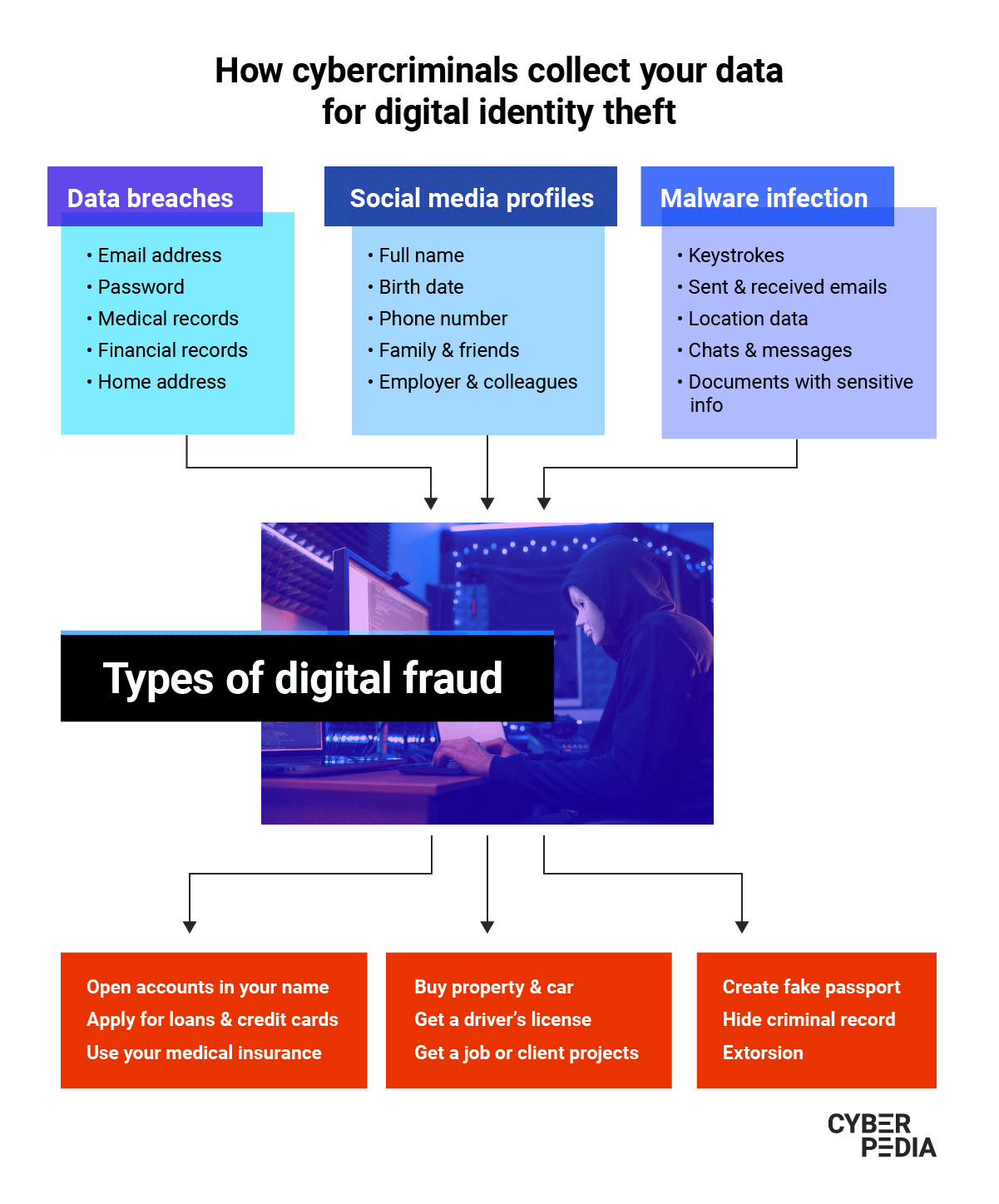
How Digital Identity Theft Happens
The tactics cyber-criminals use to steal people’s online identities are almost unlimited. Here is a list of digital identity theft tactics to watch out for:
- Pretending to be a trusted organization in fake websites and emails (phishing), text messages (SMS phishing or smishing) and phone calls (voice phishing or vishing) to trick victims into disclosing personal information (passwords, card details, answers to security questions etc.).
“Imagine a phishing email that speaks your language.
It knows exactly that you have been interested in buying a new car and the exact type of car you want. The attackers know the amount of money you’re willing to spend, they know your zip code and can even try to give you a deal that is so good you can’t resist opening the attachment or clicking on the link.
That’s really all they need: to get you to do that specific action they need.”
Liviu Arsene (Senior E-threat Analyst, Bitdefender)
- Trying multiple combinations of usernames and passwords against your accounts to gain access to them (brute-force or credential stuffing attack). Moreover, cybercriminals buy lists of hundreds of millions of leaked emails and passwords on the Dark Web.
“Besides credential stuffing, there's also the case of having a malware infection that compromises your device.
Attackers will often try to plant threats designed to collect everything you type. That means every social network account, every password, everything you type into your keyboard can potentially reach the attackers and be used to compromise all of your accounts.”
Liviu Arsene (Senior E-threat Analyst, Bitdefender)
- Using malicious links in emails, SMS, social media messages or websites to infect your devices with malware that records your keystrokes (keylogger), harvests your passwords and other sensitive data you may store on that device (spyware)
- Collecting, analyzing, and using publicly accessible data about you (OSINT - open-source intelligence) from sources such as social networks and public records to guess social security numbers and other confidential details.
- Using the same information to call your telecom provider and ask to transfer your number to a different SIM (SIM jacking). Once the transfer is complete, you lose cell phone service and the attacker can access two-factor authentication codes for your accounts, including online banking, email, and more.
- Impersonating you while calling customer service representatives in companies whose services you use. The objective is to get them to disclose your personal information and login details or change access rights to your accounts (pretexting).
“Other examples may even involve getting the victim to disclose additional information.
If they impersonate a financial officer, then attackers call their victim and ask for additional details about the particular person they’re targeting. So identity theft can be used to further additional identity theft attacks.”
Liviu Arsene (Senior E-threat Analyst, Bitdefender)
- Redirecting your emails (email hijacking) to get personal data related to credit cards, bank statements, login information and other confidential details you receive via email. They can even reply to various services, such as loan offers, in your name and send spam or phishing emails to all your contacts.
- Befriending you on social networks to influence you (social engineering) and win your trust until you share private information they can then use for identity fraud.
- Posting fake job ads to collect resumes and applications that reveal personal information such as names, home and email addresses, phone numbers and other sensitive details.
- Carrying out attacks against organizations that store and process large amounts of personal data (malicious hacking) to exfiltrate as much of it as possible (data breaches).
- Exploiting data breaches and corroborating that information with other details your digital footprint provides. The goal is to build an increasingly accurate profile of your online persona, habits and weaknesses they can later use for digital fraud.
“Cyber-criminals now gather information from websites that collect very little information up to websites that have our food ordering history. They stitch them together to create a very, very accurate mirror of what you are online.
Plus, anything is up for sale.
The most important information is the one which cannot be easily changed. Even if you can change your username or password, you cannot do the same with a social security number, your date of birth or your name. Those just stick with you for the rest of your life.
Health records are also becoming very important. This information can tell a lot about who you are, the services you are about to contract, the kind of goods on the internet you’re likely to purchase and so on. So, health records are becoming one of the most financially viable assets a cyber-criminal can collect about you.”
Bogdan Botezatu (Director of Threat Research and Reporting, Bitdefender)
What Happens to Your Information after it is Stolen
Once cyber-criminals get a hold of your information, you can’t take it back.
This is especially true for non-perishable information such as your birth date, your parents’ names, your social security number, and other details that stay the same throughout your entire life.
“The thing about identity theft is it can have a very lasting effect. You cannot control the amount of damage it produces. However, you can mitigate it.
Many people do not realize their identity has been exposed until friends contact them, telling them they have been approached by scammers, which often happens with social network account hijacks or takeovers.
Sometimes, people realize their identity has been abused when they apply for a loan for a new home or a new car and realize their credit score has plummeted.”
Bogdan Botezatu (Director of Threat Research and Reporting, Bitdefender)
Once malicious actors have your data, it goes on to live in their systems and criminal infrastructure. They trade it on the Dark Web, so it gets multiplied. It also gets assembled with other details from subsequent attacks or data leaks in a never-ending, unpredictable cycle.
While there are many elements outside your control, there is also a lot you can do to keep tabs on your digital footprint and ensure you take essential steps to protect your online privacy.
What to Do If You are a Victim of Identity Theft
Knowing what to do when you spot the signs of online identity fraud helps you act quickly to limit the damage.
Some of the immediate steps to take include:
- Taking screenshots of the affected accounts or the malicious emails and messages you received - any piece of evidence is helpful!
- Changing passwords and PINs for your essential accounts first (and then all the rest where you have used the same password or that host sensitive details)
- Contacting your bank to close accounts, cancel credit cards and take other remedial actions to stop abuse
- Getting in touch with state institutions concerned with that type of information (e.g. social security number, credit score) to flag the crooks
- Report the crime to the authorities, starting with your local law enforcement agency
To get more details, try this US federal government website dedicated to identity theft where you can notify the authorities and get a recovery plan.
How to Protect Yourself from Digital Identity Theft
Whether you want to learn how to prevent digital identity theft, to improve your online privacy or enhance your security on the Internet, the same golden principles apply.
- Keep track of your Internet-connected devices and always format them before selling or giving them away
- Maintain a list of online accounts you signed up for - this is much easier to do with a password manager!
- Use strong, unique passwords for these accounts and turn on two-factor authentication for them
- Set limits on your credit and debit cards and a credit freeze on your credit score
- Monitor your bank statements for changes each month or set up SMS alerts for transactions over a certain amount - if your bank offers the option
- Adjust the privacy and security settings for your most important accounts (Google, Facebook etc.)
- Periodically remove all unnecessary applications from your devices and never install apps outside the official app stores
- Back up all your important assets on an external hard drive or in the cloud (encrypted) or, ideally, both
- Update all software applications across your devices (from laptops to smartphones and the apps on it to your internet-connected TV)
- Install a security solution on all the devices that support it and set regular scans to run automatically
- Start using Bitdefender Digital Identity Protection to get alerts when malicious actors use your email addresses, when your data leaks on the dark web or when social media impersonators try to use your good reputation for fraud.
- Activate Bitdefender Identity Theft Protection, a one-stop credit monitoring and identity theft protection service, to avoid damages and financial losses.
- Keep reading about online security and privacy on the internet to strengthen your digital savviness!
Every time you use a stronger password, every time you ask yourself “why am I getting this request?”, every time you think twice about posting a picture of your home, you make it a bit more difficult for cyber-criminals to steal your digital identity.
If you think about it, that kind of makes you your own superhero. You are certainly ours for taking the time to read - and hopefully apply - this guide!
tags
Author
Choose what the experts use. Award-winning cybersecurity you can trust and rely on.
View all posts

