What Is Data Encryption? (And Why Experts Love It)

When deciding to improve your online privacy and security it is vital to take action right away. Although terms like “data encryption” and “security protocols” can be a bit difficult to understand, they are vital for keeping your digital footprint safe.
Now you have our very own cybersecurity experts explain what data encryption is and why it plays such an important role in our digital lives.
What Is Data Encryption? A Definition
Data encryption is the process of using a private key to convert data into an unreadable format, so no one else can read it, except for the owner of that private key.
Because it prevents unauthorized parties from viewing the data, encryption is one of the essential technology layers that protect millions of people around the world.
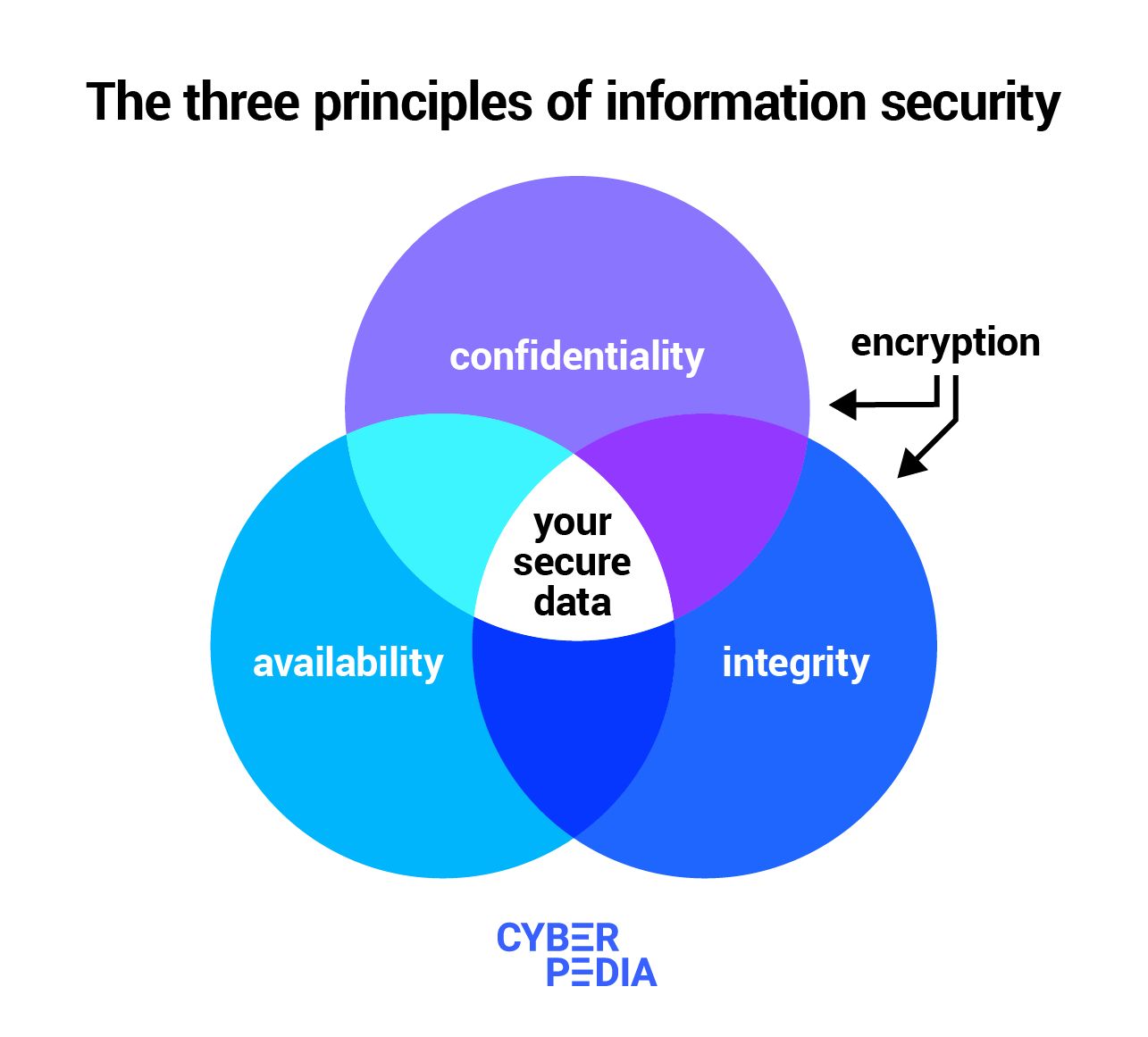
Three principles form the foundation of information security:
- Confidentiality ensures that authorized users and processes are the only ones that can access or modify data;
- Integrity makes sure data is maintained in a correct state so no one and nothing can modify it by accident or with malicious intentions;
- Availability ensures authorized users have access to the data whenever they need to.
Data encryption is highly effective for two reasons:
First, because it covers two out of three of these principles, making information both confidential and keeping its integrity. For example, because cryptographic keys validate that you are who you say you are, they give you the right to view the data and participate in conversations protected by encryption.
Second, encryption is an efficient method to increase and preserve security and privacy online because current-day computer systems do not have enough computing power to crack it.
Data Encoding vs Data Encryption
Although a common mistake to make, data encoding is not the same as data encryption.
Encoding uses a specific code (letters, symbols, and numbers) to convert data into a format that a different type of system can consume. For example, think how you can store and access music on your computer, on an mp3 player, CD or vinyl.
In technology, encoding keeps the data usable because decoding it is a matter of using the same code used in the beginning to reverse the process. Encoding standards are public, so anyone can use them to decode the data.
This makes encoding very different from encryption. The goal of encryption is to keep data secret from others, except for the intended recipient. In this context, only specific individuals can decrypt the data.
How Data Encryption Really Works
Let’s look at how data encryption keeps snoopers and hackers from intercepting and accessing your information when it is most exposed: while it travels across the Internet.
Before we jump into specifics, let’s pin down a few definitions for clarity. Now that you already know what encryption is, here are a few more useful terms:
- Cryptography - the study and practice of methods to secure communication to keep it private from prying eyes and malicious interference
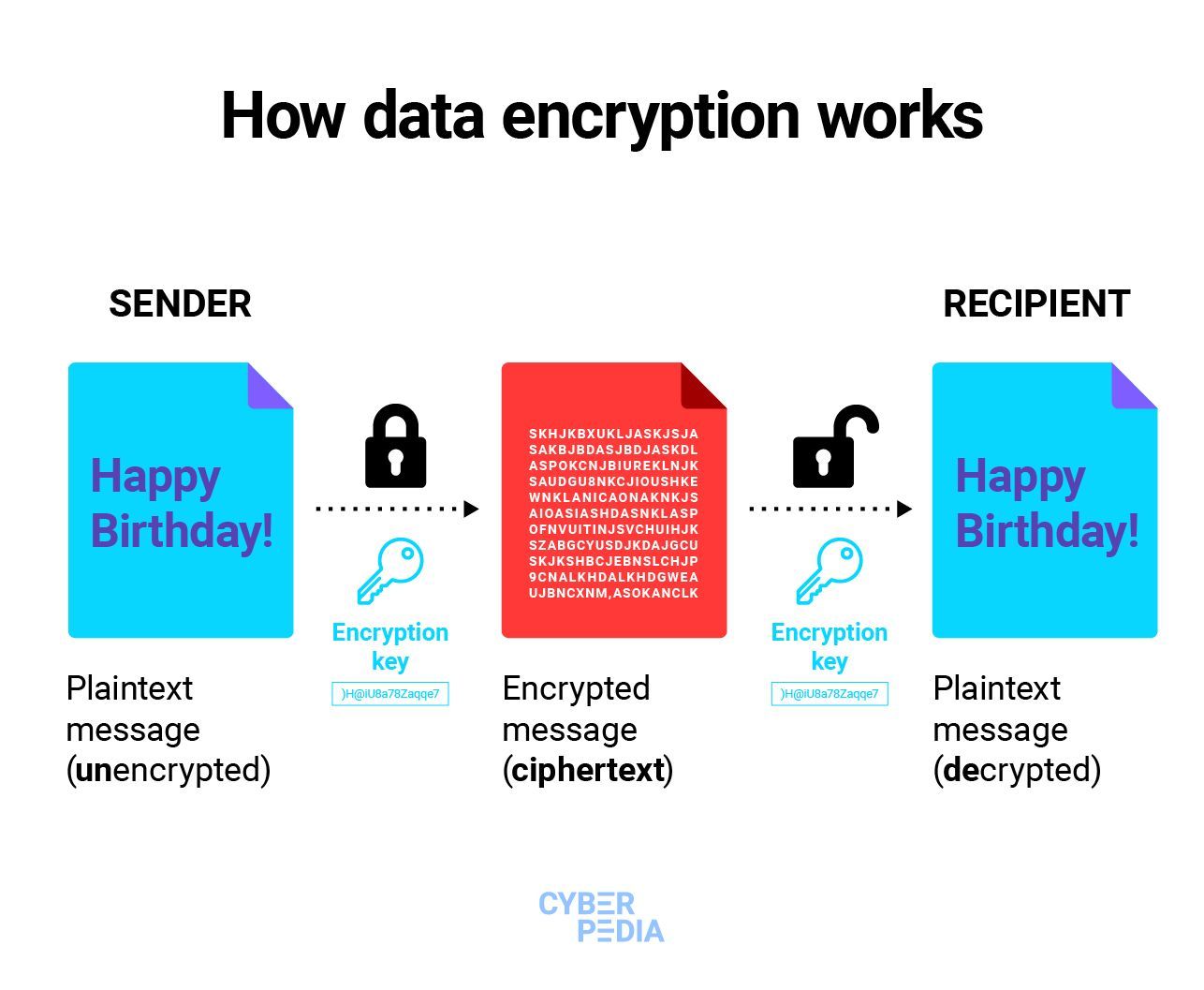
- Plaintext - the original, unencrypted state the information is in
- Ciphertext - the encrypted information
- Encryption key - the piece of information (a random string of numbers, letters, and symbols) that a cryptographic algorithm uses to encrypt and decrypt data. The strongest encryption keys are unique, unpredictable, and as long as current technology allows it.
- Encryption algorithm - the method that uses the encryption key to transform plaintext into ciphertext, so it appears random to unauthorized users but decipherable to the intended recipient; using the decryption key makes the encrypted data readable again.
"Why is data encryption necessary?" you might ask. "It seems a bit of a headache to deal with."
Because we transact so much confidential data through computer systems and transfer it over the Internet, encryption is vital for protecting it. Without it, anyone with the necessary resources and know-how could:
- Identify and steal all your passwords, including those for online banking, health insurance, and other accounts essential for your life;
- Access and capture your SSN, card details, tax records, medical records, and a range of other details an attacker could use against you for digital identity theft, among other types of fraud;
- Pinpoint your real-time location with accuracy and track your every move - not just in the online world but in the physical one as well;
- Read all your conversations (from emails to messages you exchange on social media platforms) and change their contents by including links that lead to infected websites, for example.
The good news is that, whether you shop online, share pictures via private messages, or transfer sensitive files to someone, you already use encryption every day.
"Most of the conversations on the Internet are transparently encrypted and decrypted without us having to do anything with it. And, of course, you can kick your security awareness up a notch."
Bogdan Botezatu (Director of Threat Research and Reporting, Bitdefender)
Encrypting Data at Rest or Data in Transit
Data at rest is the information you store on your device, whether it is your laptop, phone, a flash drive, external storage, or memory cards. Think pictures, music, and the large collection of miscellaneous files we all have (including those ebooks we said we would read).
Because you do not actively send this data over the Internet, you may think it is safer. However, attackers intend to exploit the situation by trying to infect your device and find a way to harvest that data.
Encrypting the data at rest protects it if you lose your device, if it gets stolen, or if an unauthorized person tries to access it without your permission or knowledge.
Data in transit is data that is actively traveling through the Internet or through private networks (e.g. intranets that companies have). Because your data flows through so many systems and organizations, it is more vulnerable to interception, surveillance, manipulation, and attack.
Encrypting data in transit ensures that, while it moves from your end to the intended recipient, no one can see or modify your data.
Think of how we used to go to the bank or the ATM for all our money-related transactions. For many today, most of those activities now happen online.
While a bank can create a safe environment in its local branch (cameras, secure access, security personnel), it can only do so much to keep you safe when you log into their online banking app.
The bank can use HTTPS, which indicates your connection to their website is encrypted, it can validate your identity through a code sent through SMS or your fingerprint (besides or instead of a password). However, it cannot ensure you do not have malware on your device, that someone is not looking over your shoulder when you type your credentials, or that an attacker is not monitoring your device through the unprotected Wi-Fi network you are using.
Always try to keep your data safe. If you are looking to protect data that sits on your device (data at rest), consider using a trustworthy encryption software.
If you need to be sure your data is always encrypted, no matter the type of connection you are on (public Wi-Fi, home Wi-Fi, 4G), using a secure VPN can be the most effective solution. You can set it to run at startup, which makes it the “set and forget” security layer that does all the work for you.
Find out more on how to use your VPN like an expert.
What Are the Advantages of Data Encryption?
In the world of technology, there is no better way of protecting data from unauthorized access or theft than encryption.
Due to the complexity of the mathematical process involved, cybersecurity specialists can secure sensitive personal information such as your Social Security number, birth date and medical records.
Websites and apps use encryption to maintain data security and privacy for financial transactions, online shopping, storing and sharing confidential documents, online banking, and sending sensitive data to trusted sources like medical clinics.
Most of these activities use encryption as a default. However, because this type of data (financial, medical, commercial) is a lucrative business for cyber-criminals and snoopers, they will actively seek to bypass this security layer.
How to Encrypt Your Internet Traffic to Keep Your Data Safe
Just like your data, you are most exposed while on the go. Since not all websites use encryption (which is especially true for malicious sites that cyber-criminals control), your best course of action is to add your own encryption layer.
This does not involve any kind of complex tech, nor does it require expert abilities. Literally anyone can use it.
With just a few clicks to get set up, you can turn on your secure connection with Bitdefender Premium VPN. It gives you unlimited encrypted traffic, no matter the network you are connected to. You will find it especially helpful when you need to use unprotected WiFi hotspots and are worried about your privacy and security.
Why Encryption is Good for Your Data
Data encryption has helped create a structurally stronger Internet. Its role is bound to become even more important for overcoming the obstacles of a digital age more extensive than anyone can imagine.
But we must also remember that cyber-criminals leverage encryption as well. In their ransomware attacks, they turn victims’ data into ciphertext and extort them for money in exchange for the decryption key.
So it is wise to incorporate tools like a secure VPN, digital identity protection services, and anti-malware solutions into your setup. Or even try an all-in-one protection mega-suite which includes them all.
Besides benefiting from the good kind of encryption, when these tools work together, they boost each other’s benefits and have an even stronger positive impact on your online safety.
tags
Author
Choose what the experts use. Award-winning cybersecurity you can trust and rely on.
View all posts