Bitdefender Threat Debrief | September 2022

MDR Insights
What are hybrid attacks?
In the last few years, we have seen a dramatic shift in the level of sophistication of cyber attacks, mostly thanks to the introduction of the profit-sharing business model for financially motivated threat actors. Phishing attacks and leaked/weak credentials are still dominating the initial compromise vector, but the number of security breaches caused by vulnerability exploits has doubled in the last year (source: Data Breach Investigations Report 2022). This trend can be explained by the increased popularity of hybrid attacks – a type of attack where the initial compromise is opportunistic and relies on automated scanners but is then triaged by a human operator to determine if it’s worth further development.
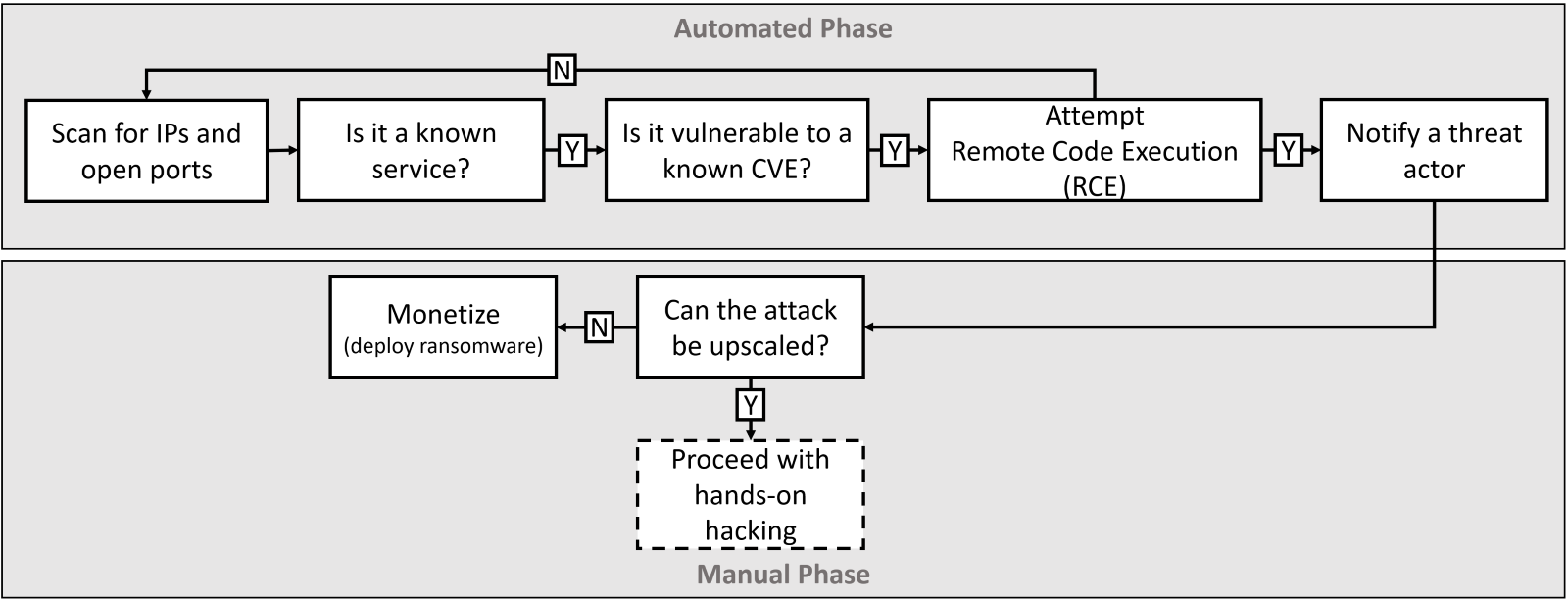
Hybrid attacks are on the rise, combining the automated initial compromise
with hands-on triage.
This expansion of attacks can take different forms – for example, even a small company can have highly valuable data (lawyers working with celebrities/politicians or a third-party contractor with insider access). A company can be part of the supply chain for a much larger corporation –it is often not what you have that’s valuable to threat actors, it is whom you know and are connected to. To learn more about these kinds of attacks, you can read our Deep Dive into a Corporate Espionage Operation – an analysis by our own Bitdefender Labs of an industrial espionage operation targeting a small technology company based in the United States.
Ransomware Report
Spear phishing attacks are often used as an initial attack vector and ransomware infection is often the final stage of the kill chain. For this report, we analyzed malware detections collected in August 2022 from our static anti-malware engines. Note: we only count total cases, not how monetarily significant the impact of infection is. Opportunistic adversaries and some Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) groups represent a higher percentage compared to groups that are more selective about their targets, since they prefer volume over higher value.
When looking at this data, remember these are ransomware detections, not infections.
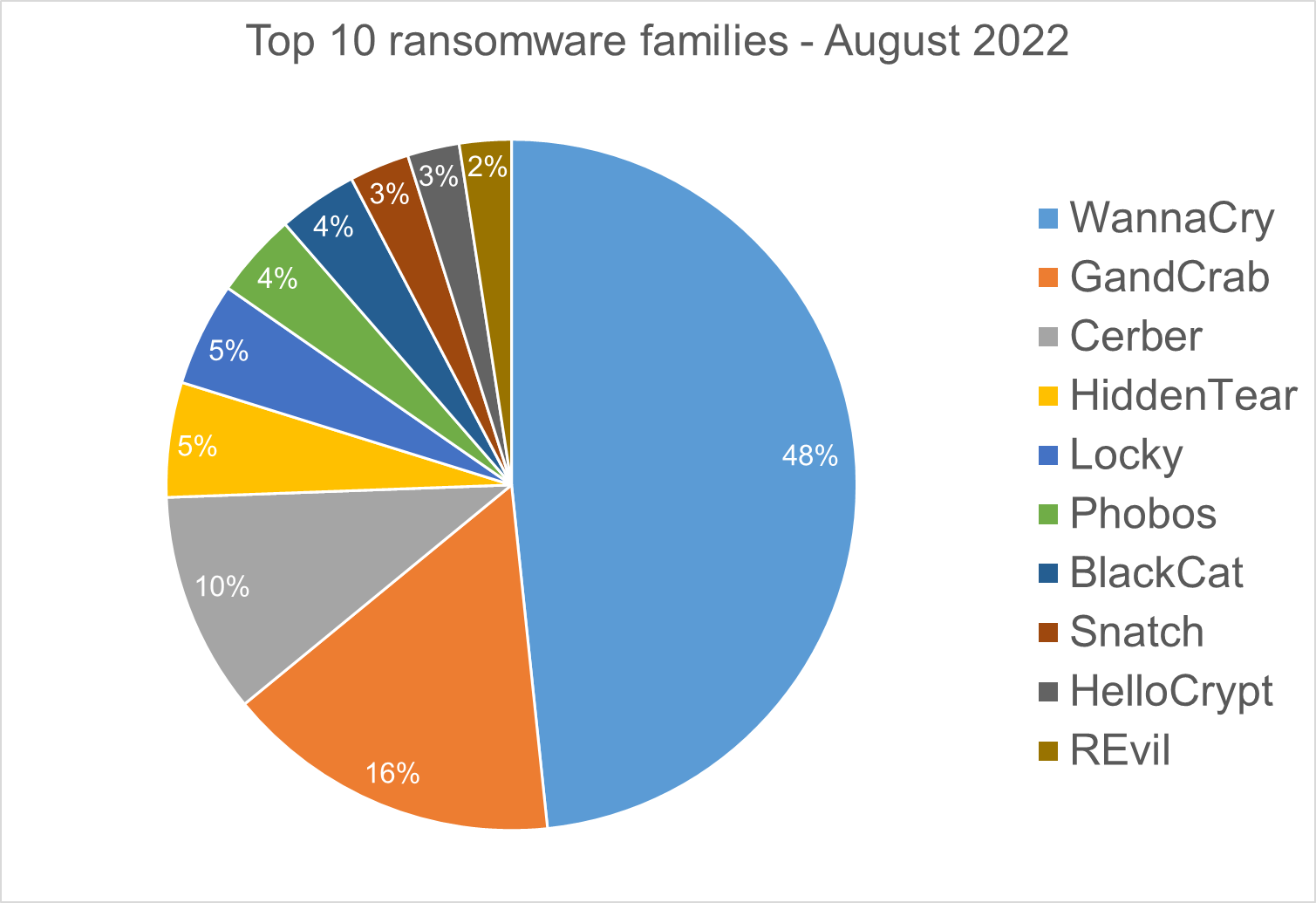
Top 10 Ransomware Families
We analyzed malware detections from August 1 to August 31. In total, we identified 193 ransomware families. Number of detected ransomware families can vary each month, depending on the current ransomware campaigns in different countries.
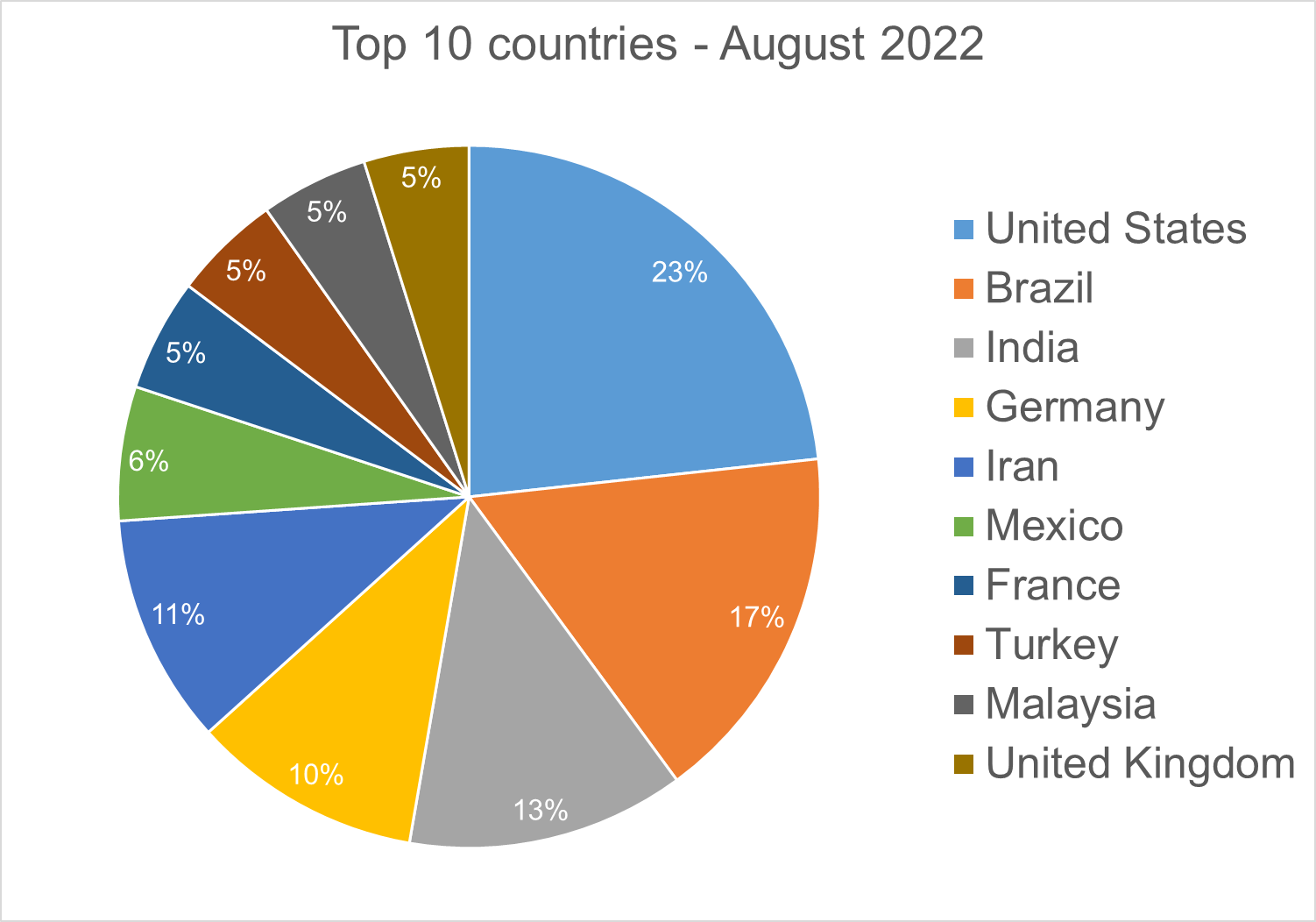
Top 10 Countries
In total, we detected ransomware from 148 countries in our dataset this month. Ransomware continues to be a threat that touches almost the entire world. Below is a list of the top 10 countries most impacted by ransomware. Many ransomware attacks continue to be opportunistic, and the size of population is correlated to the number of detections.
Android trojans
Below are the top 10 trojans targeting Android we have seen in our telemetry during August 2022.
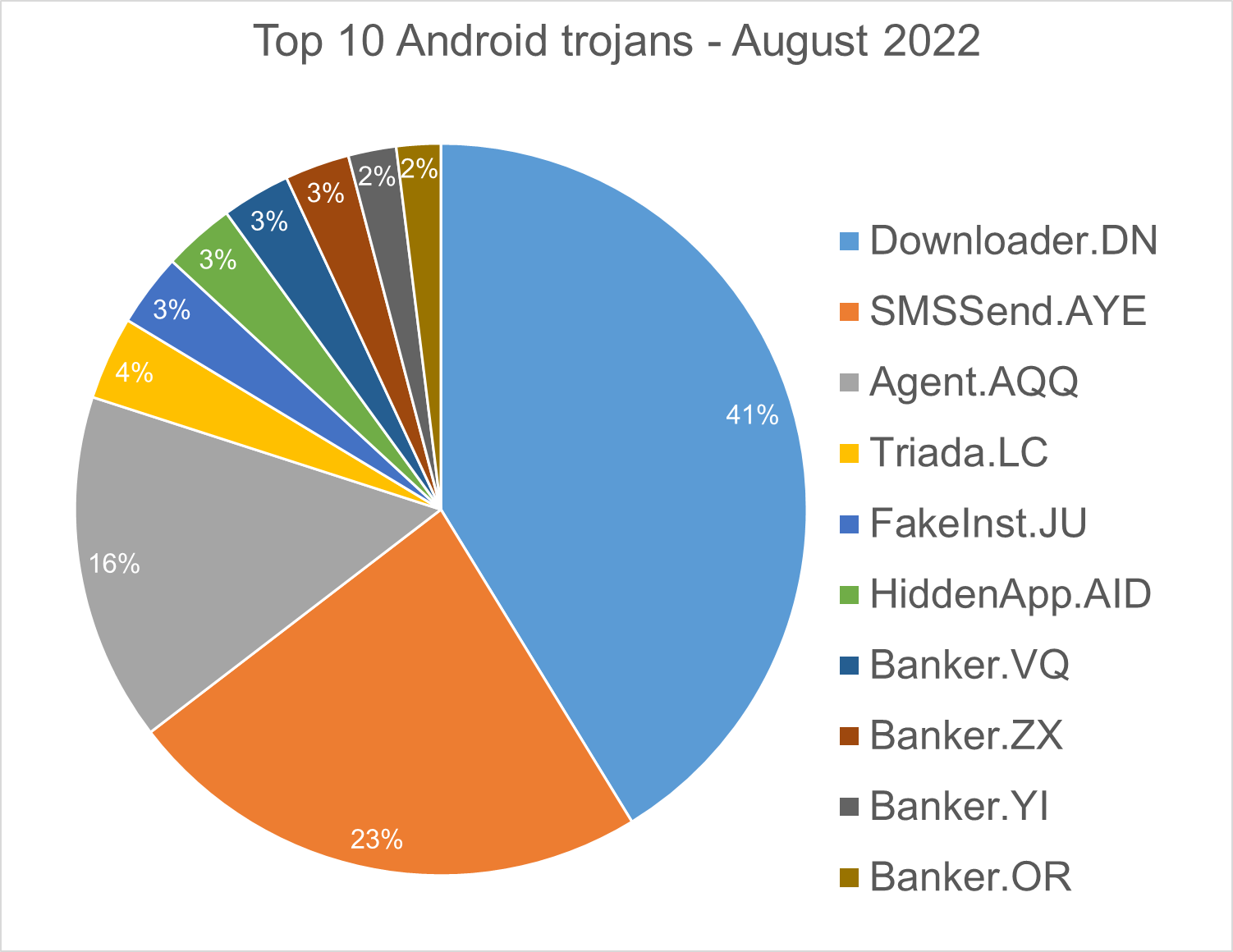
Downloader.DN – Repacked applications taken from Google App Store and bundled with aggressive adware. Some adware downloads other malware variants.
SMSSend.AYE - Malware that tries to register as the default SMS application on the first run by requesting the consent of the user. If successful, it collects the user's incoming and outgoing messages and forwards them to a Command & Control (C&C) server.
Agent.AQQ - A dropper malware is a trojan that hides the dangerous payload inside an app as an evasion technique. If it can avoid security defenses, this payload is deployed. The malicious payload is decrypted and loaded by the dropper.
Triada.LC – Malware that gathers sensitive information about a device (Device IDs, Subscriber IDs, MAC addresses) and sends them to a malicious C&C server. The C&C server responds by sending back a link to a payload which the malware downloads and executes.
FakeInst.JU – Malware that has the capability to read and send text messages. A text message is sent to a premium number every 1000 seconds. After deployment, it hides its icon from the application menu, and sends sensitive data from the phone (IMEI, phone number, network info…) to a remote server.
HiddenApp.AID - Aggressive adware that impersonates AdBlock applications. When running for the first time, it asks permission to display on top of other apps. With this permission, the application can hide from the launcher.
Banker.VQ, OR - Applications that drop and install encrypted modules. This trojan grants device admin privileges, and gains access to manage phone calls and text messages. After deploying, it maintains a connection with the C&C server to receive command and upload sensitive information.
Banker.ZX – Applications that disguise themselves as banking apps and can imitate conversation with customer support. When the malware runs for the first time, it asks for permissions to access contacts, microphone, geolocation, and camera. Once the permissions are granted, the malware can receive commands from the C&C server to exfiltrate sensitive data from the phone.
Banker.YI - Polymorphic applications that impersonate legit apps (Google, Facebook, Sagawa Express ...). Once installed, it locates banking applications installed on the device and tries to download a trojanized version from the C&C server.
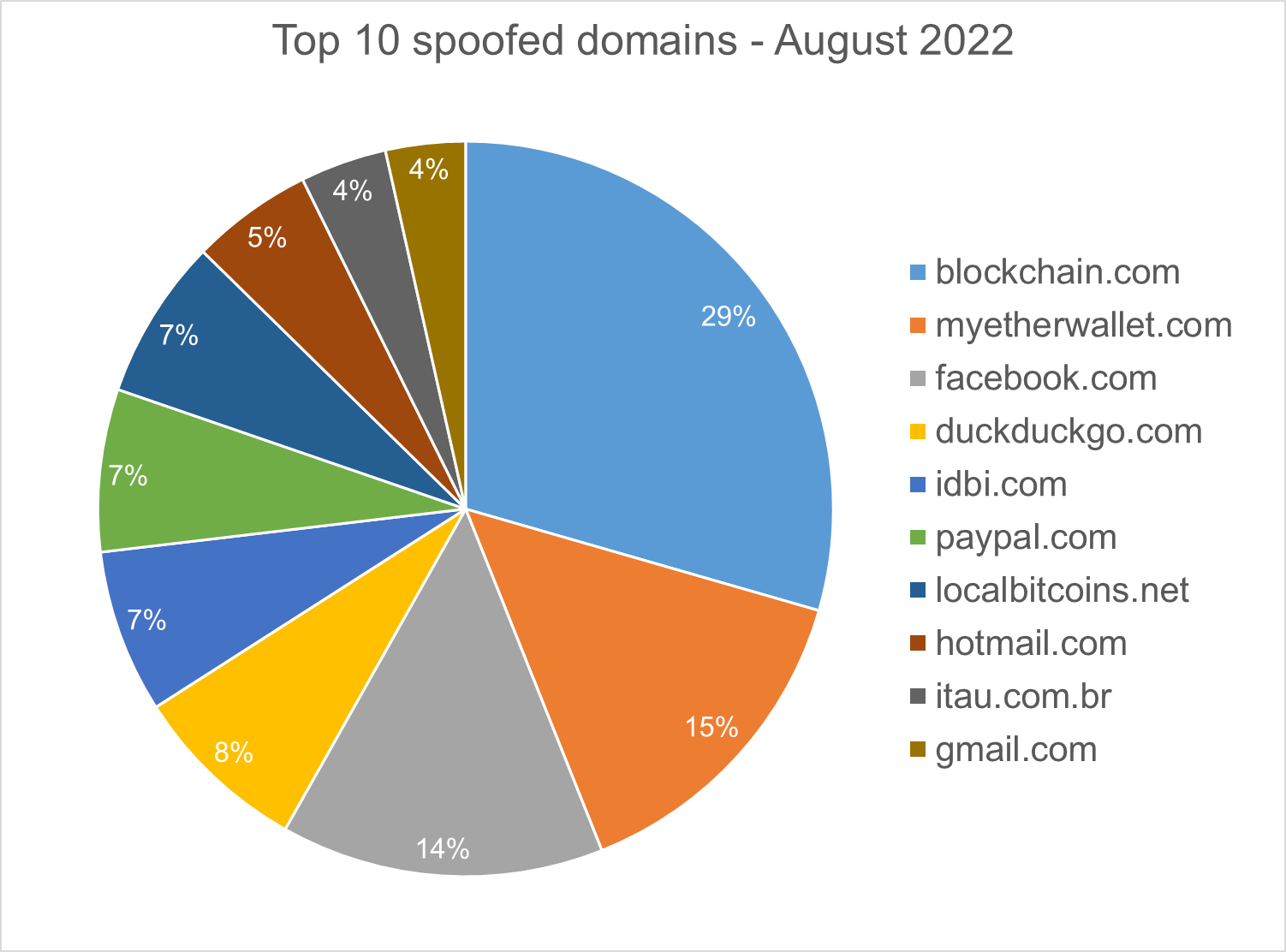
Homograph Phishing Report
Homograph attacks work to abuse international domain names (IDN). Threat actors create international domain names that spoof a target domain name. When we talk about “target” of IDN homograph phishing attacks, we refer to the domain that threat actors are trying to impersonate. You can read more about this type of attack in one of our previous reports.
Below is the list of the top 10 most common targets for phishing sites.
About Bitdefender Threat Debrief
The Bitdefender Threat Debrief (BDTD) is a monthly series analyzing threat news, trends, and research from the previous month. Don’t miss the next BDTD release, subscribe to the Business Insights blog, and follow us on Twitter. You can find all previous debriefs here.
Bitdefender provides cybersecurity solutions and advanced threat protection to hundreds of millions of endpoints worldwide. More than 150 technology brands have licensed and added Bitdefender technology to their product or service offerings. This vast OEM ecosystem complements telemetry data already collected from our business and consumer solutions. To give you some idea of the scale, Bitdefender Labs discover 400+ new threats each minute and validate 30 billion threat queries daily. This gives us one of the industry’s most extensive real-time views of the evolving threat landscape.
We would like to thank Bitdefenders Tyler Baker, Alin Damian, Mihai Leonte, Andrei Mogage, Sean Nikkel, Nikki Salas, Rares Radu, Ioan Stan, Marius Tivadar, and Horia Zegheru (sorted alphabetically) for their help with putting this report together.
tags
Author

Martin is technical solutions director at Bitdefender. He is a passionate blogger and speaker, focusing on enterprise IT for over two decades. He loves travel, lived in Europe, Middle East and now residing in Florida.
View all postsRight now Top posts
FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Don’t miss out on exclusive content and exciting announcements!
You might also like
Bookmarks











