This guide explains how to flush the DNS cache and reset an internet connection on both Windows and Mac.
What is DNS cache?
Your computer stores DNS (Domain Name System) information locally so it doesn’t need to ask a DNS server every time you visit a website. This is called the DNS cache, and it helps speed up browsing.
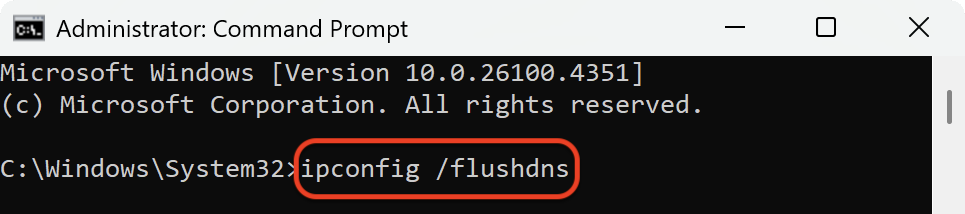
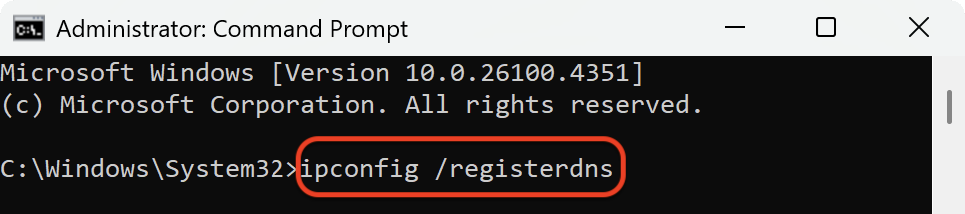
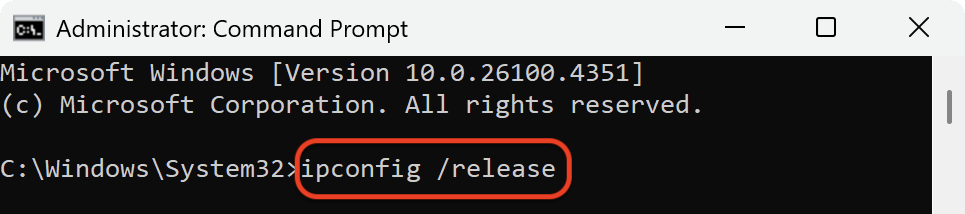
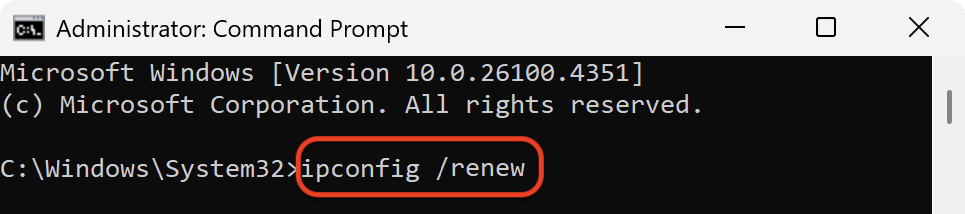
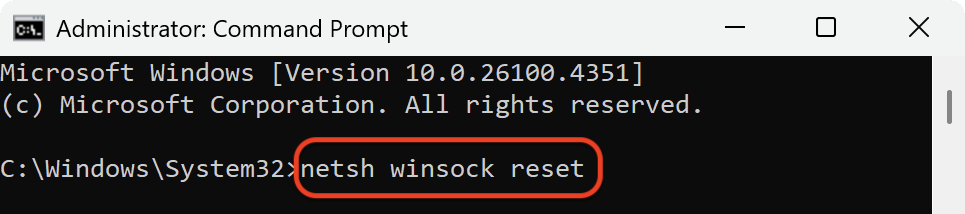
However, cached records can become outdated or corrupted. When this happens, you might see errors such as pages not loading, DNS server not responding, or trouble connecting to certain sites. Flushing the DNS cache clears out the stored records and forces your device to request fresh information from the DNS server. In addition, resetting your network connection through commands like ipconfig /release, ipconfig /renew, and a Winsock reset helps fix communication issues between your device and the internet.
How to flush DNS cache on Windows
How to flush DNS cache on Mac
Flushing the DNS and resetting the network connection often solves most connectivity issues. If issues continue, you may need to restart your router or check with your Internet Service Provider (ISP).